Introduction
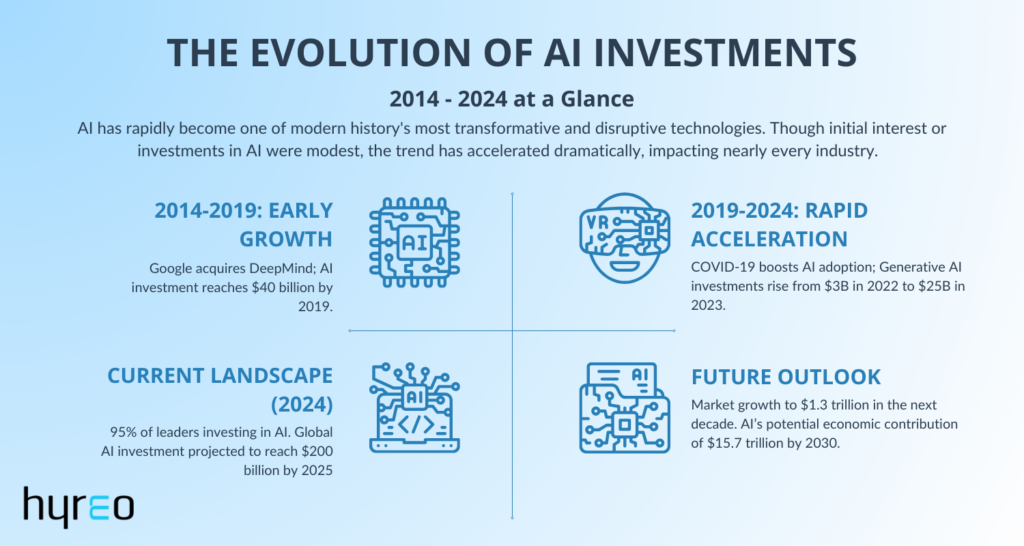
AI has rapidly become one of modern history’s most transformative and disruptive technologies. Though initial interest or investments in AI were modest, the trend has accelerated dramatically, impacting nearly every industry.
At present, leaders and investors have a clear picture of what lies ahead and the potential economic growth AI technologies could bring in the upcoming years. As a result, there is now greater confidence in investing in and experimenting with AI, recognizing its role in fueling innovation and business expansion.
A recent report from CNBC highlights this growing trend, noting that not only venture capitalists but also tech giants like Microsoft and Amazon are pouring billions into capital-intensive AI companies such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Scale AI, and CoreWeave.
To provide a bird’s-eye view of recent AI investments, we’ve compiled key highlights of AI-focused funding, outlining the growth trajectory over the past decade.
Investments in AI: The First Half (2014 – 2019)
In the early years of the decade, people and organizations were skeptical about AI’s potential. However, as its ability to drive business efficiency became more apparent, companies increasingly began investing in AI to expand their client base and quickly generate new revenue streams. This shift was particularly evident among technology organizations.
A notable example is Google’s acquisition of DeepMind, a British-American artificial intelligence research lab, in 2014, and its eventual merging with Google AI’s Google Brain—an effort to leverage AI for competitive advantage.
Over the next two years, early adopters of AI ramped up their investments by launching initiatives that yielded positive returns. By 2017, McKinsey’s Global Survey on AI found that the adoption rate of AI technologies had doubled, with 50% to 60% of companies increasing their AI investments. Notably, leaders who achieved the highest financial returns from AI invested even more to scale their operations.
By 2018, 40% of companies reported allocating more than 5% of their digital budgets to AI. Industries like manufacturing and risk management experienced the most significant revenue impacts from AI adoption.
Additionally, CSET’s Tracking AI Investment report revealed that by the end of 2019, privately held AI companies had attracted nearly $40 billion in disclosed equity investments, with U.S. companies accounting for $25.2 billion of that total.
Also read: Root Causes of Gen AI POC Pilot Failures in Tech Firms
Investments in AI: The Second Half (2019- 2024)
The unexpected pandemic followed by a sudden shift to a remote work culture further accelerated the growth of AI, attracting more investments. Apparently, 41% of companies improved their AI strategies during COVID-19, as per Appen’s State of AI 2020 report.
According to a 2021 #Gartner survey, 33% of technology providers planned to invest $1 million or more in AI by 2023. AI technologies received the second-highest mean funding allocation compared to other emerging technology areas like cloud computing and IoT.
The survey also highlighted AI development as cost-intensive since most funding amounts by respondents’ companies were equal to or greater than $250,000 for AI technologies.
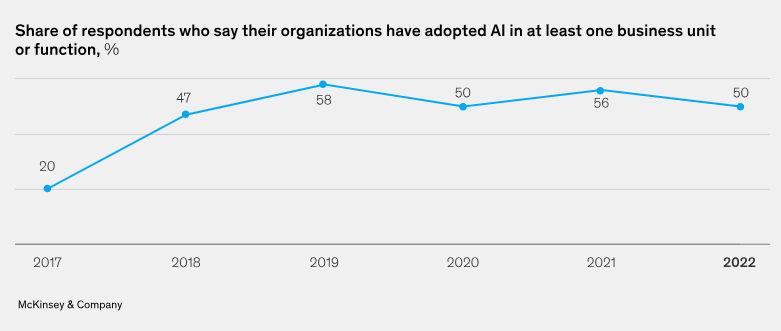
By 2022, global AI adoption had reached 2.5 times the rate seen in 2017, although the trend began to level off between 2019 and 2022.
(Source: Mckinsey)
McKinsey’s 2022 report also revealed that while only 40% of respondents had previously allocated at least 5% of their digital budgets to AI, today over 50% report committing at least that level of investment or more.
An explosive growth occurred when Generative AI emerged and started gaining traction in 2023, where 40% of respondents in McKinsey’s 2023 Global survey admitted expressing increased interest in boosting AI investments due to advancements in Generative AI.
According to the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI), Global private investment in generative AI peaked, rising from $3 billion in 2022 to $25 billion in 2023. Not only that, 80% of Fortune 500 earnings calls mentioned AI.
The EY CEO Outlook Pulse survey revealed that a vast majority of CEOs (88%) are incorporating AI into their capital allocation strategies. Of those, 43% are already making active investments in AI, while an additional 45% plan to make substantial AI investments within the next 12 months.
With Generative AI coming into the picture, saving and scaling businesses, the percentage of organizations using Gen AI regularly doubled within just a ten-month timeframe, as per the Global Survey on AI conducted by McKinsey in 2024. It became common in business functions, generating the most value specifically in marketing/sales and product/service development.
Also read: Transformative Future Powered by Autonomous AI Agents
Investments in AI: 2024 and Beyond
As 2024 dawned, a significant increase in AI investments was spotted, as highlighted by the EY AI Pulse survey. According to the survey, 95% of senior leaders are currently investing in AI, and the number of companies investing $10 million or more is expected to double by 2025.
This upward trend aligns with a Bloomberg Intelligence report, which projects that the Generative AI market is on the verge of exponential growth. It is expected to soar from a market size of $40 billion in 2022 to $1.3 trillion over the next decade, further manifesting AI’s profound impact on business innovation and scalability.
Key Statistics on AI Investments for 2024 and beyond
- By 2025, global #AIinvestment is projected to reach $200 billion. (SAP)
- OpenAI leads the industry with a $14 billion investment. (Stocklytics)
- The United States has invested the most in AI, with $328.5 billion. (AIPRM)
- AI is expected to contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, surpassing the current output of China and India combined. (Forbes)
- AI could add $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually to the worldwide economy. (McKinsey)
- The global AI market size was estimated at USD 196.63 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 36.6% from 2024 to 2030. (Grand View Research)
Top Industries Leading AI Investment
The top 10 industries that welcomed significant AI investments over the past decade:
- Healthcare
- Finance
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
- Education
- Agriculture
- Entertainment
- Telecommunications
- Energy
Also read: The Definitive Guide to Conversational AI & Candidate Experiences
Challenges of Investing in AI
Immaturity of AI technologies: Gartner points out technology immaturity as the major hindrance to AI adoption as their survey found AI technologies still being in development along with product complexity and lack of skills as other crucial challenges.
Infrastructural Inadequacies: EY finds a lack of a strong data structure, an AI governance framework, and skill gaps as primary factors that limit organizations’ efforts to maximize AI’s full potential.
Data protection & Privacy: Data security is another cause of concern for AI’s enterprise readiness, as emphasized by SAP. Many organizations have put restrictions on the use of Gen AI tools, fearing the disclosure of confidential/financial information of companies.
Conclusion
The transformative potential of AI in revolutionizing industries is clearer than ever. Looking back over the past decade, it’s evident that initial hesitation has diminished, making way for mass adoption, which is imminent once the challenges hindering further AI investments are addressed. As organizations increasingly recognize AI’s potential, competition for the best technologies will intensify. Any organization that lags in adopting AI, regardless of its industry, risks falling behind. Therefore, making calculated investments and embracing AI advancements has never been more crucial.
As an AI-powered recruiter co-pilot, we understand this and are actively leveraging AI for various recruitment use cases. By utilizing Generative AI for critical recruiting functions such as candidate profiling, pre-screening, and conversational agents, we have already driven transformative results for some top global brands. Our predictive algorithms offer over 90% accuracy in joining propensity predictions, providing recruiters with valuable insights to make smart, data-driven hiring decisions.
Curious to see more of our AI innovations? Visit HyreoLabs
FAQs
- What are the main drivers of AI investments over the past decade?
The rise in AI investments is driven by advancements in technology, increasing data availability, and growing demand for automation across various industries.
- How have AI investments impacted businesses and industries?
AI investments have led to enhanced operational efficiency, innovation, and new revenue streams, transforming industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail.
- What future trends are expected in AI investments?
Future trends include a greater focus on ethical AI, integration with other emerging technologies, and continued growth in sectors like autonomous systems and personalized experiences.



